Credits: Raschka, chap. 12
12. PyTorch Pre-flight#
Note that the optional watermark extension is a small IPython notebook plugin that I developed to make the code reproducible. You can just skip the following line(s).
from IPython.display import Image as IPythonImage
%matplotlib inline
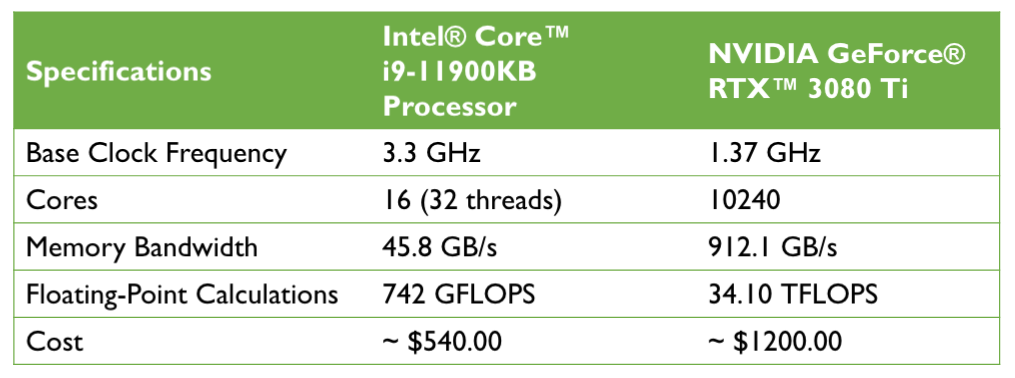
12.1. Performance challenges#
12.2. First steps with PyTorch#
12.3. Installing PyTorch#
%pip install torch
Requirement already satisfied: torch in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (2.4.1+cu121)
Requirement already satisfied: filelock in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from torch) (3.16.1)
Requirement already satisfied: typing-extensions>=4.8.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from torch) (4.12.2)
Requirement already satisfied: sympy in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from torch) (1.13.3)
Requirement already satisfied: networkx in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from torch) (3.3)
Requirement already satisfied: jinja2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from torch) (3.1.4)
Requirement already satisfied: fsspec in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from torch) (2024.6.1)
Requirement already satisfied: MarkupSafe>=2.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from jinja2->torch) (2.1.5)
Requirement already satisfied: mpmath<1.4,>=1.1.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from sympy->torch) (1.3.0)
import torch
import numpy as np
print('PyTorch version:', torch.__version__)
np.set_printoptions(precision=3) # sets the precision of the printed numbers to three decimal places
PyTorch version: 2.4.1+cu121
# Check if GPU is available
if torch.cuda.is_available():
print("GPU is available!")
print(f"Using GPU: {torch.cuda.get_device_name(0)}")
else:
print("GPU not available, using CPU.")
GPU not available, using CPU.
! python -c 'import torch; print(torch.__version__)'
2.4.1+cu121
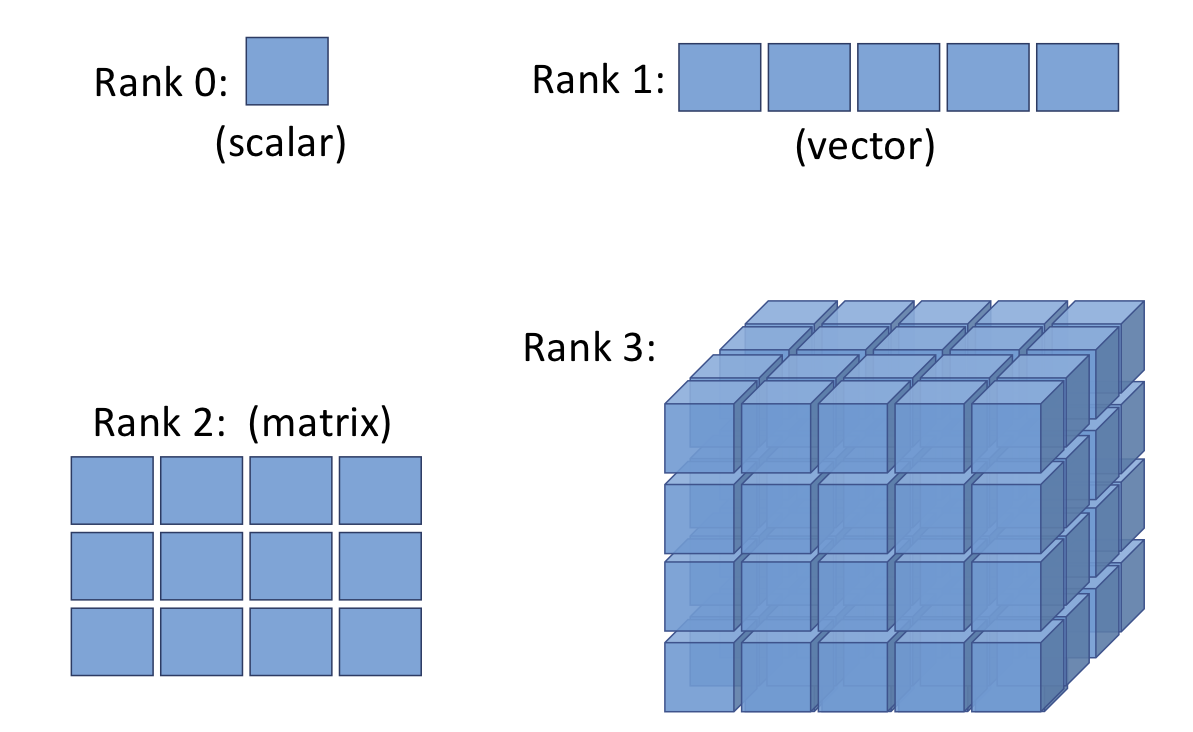
12.4. Creating tensors in PyTorch#
a = [1, 2, 3]
b = np.array([4, 5, 6], dtype=np.int32)
t_a = torch.tensor(a)
t_b = torch.from_numpy(b)
print(t_a)
print(t_b)
tensor([1, 2, 3])
tensor([4, 5, 6], dtype=torch.int32)
torch.is_tensor(a), torch.is_tensor(t_a)
(False, True)
t_ones = torch.ones(2, 3)
t_ones.shape
torch.Size([2, 3])
print(t_ones)
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
rand_tensor = torch.rand(2,3)
print(rand_tensor)
tensor([[0.7757, 0.8721, 0.0653],
[0.3834, 0.7023, 0.5269]])
12.5. Manipulating the data type and shape of a tensor#
t_a_new = t_a.to(torch.int64)
print(t_a_new.dtype)
torch.int64
t = torch.rand(3, 5)
t_tr = torch.transpose(t, 1, 0)
print(t.shape, ' --> ', t_tr.shape)
torch.Size([3, 5]) --> torch.Size([5, 3])
print(t)
print(t_tr)
tensor([[0.6410, 0.1115, 0.8881, 0.6447, 0.7698],
[0.8651, 0.5794, 0.5739, 0.7982, 0.4404],
[0.4984, 0.3944, 0.1634, 0.2508, 0.7270]])
tensor([[0.6410, 0.8651, 0.4984],
[0.1115, 0.5794, 0.3944],
[0.8881, 0.5739, 0.1634],
[0.6447, 0.7982, 0.2508],
[0.7698, 0.4404, 0.7270]])
t = torch.zeros(30)
t_reshape = t.reshape(5, 6)
print(t_reshape.shape)
torch.Size([5, 6])
t = torch.zeros(1, 2, 1, 4, 1)
t_sqz = torch.squeeze(t, 2)
print(t.shape, ' --> ', t_sqz.shape)
print(t)
print(t_sqz)
torch.Size([1, 2, 1, 4, 1]) --> torch.Size([1, 2, 4, 1])
tensor([[[[[0.],
[0.],
[0.],
[0.]]],
[[[0.],
[0.],
[0.],
[0.]]]]])
tensor([[[[0.],
[0.],
[0.],
[0.]],
[[0.],
[0.],
[0.],
[0.]]]])
12.6. Applying mathematical operations to tensors#
torch.manual_seed(1)
t1 = 2 * torch.rand(5, 2) - 1
t2 = torch.normal(mean=0, std=1, size=(5, 2))
print(t1)
print(t2)
tensor([[ 0.5153, -0.4414],
[-0.1939, 0.4694],
[-0.9414, 0.5997],
[-0.2057, 0.5087],
[ 0.1390, -0.1224]])
tensor([[ 0.8590, 0.7056],
[-0.3406, -1.2720],
[-1.1948, 0.0250],
[-0.7627, 1.3969],
[-0.3245, 0.2879]])
t3 = torch.multiply(t1, t2)
print(t3)
tensor([[ 0.4426, -0.3114],
[ 0.0660, -0.5970],
[ 1.1249, 0.0150],
[ 0.1569, 0.7107],
[-0.0451, -0.0352]])
t4 = torch.mean(t3, axis=0)
print(t4)
tensor([ 0.3491, -0.0436])
t4_b = torch.mean(t3, axis=1)
print(t4_b, t4_b.shape)
tensor([ 0.0656, -0.2655, 0.5699, 0.4338, -0.0402]) torch.Size([5])
print(t1.shape, t2.shape)
torch.Size([5, 2]) torch.Size([5, 2])
t5 = torch.matmul(t1, torch.transpose(t2, 0, 1))
print(t5)
tensor([[ 0.1312, 0.3860, -0.6267, -1.0096, -0.2943],
[ 0.1647, -0.5310, 0.2434, 0.8035, 0.1980],
[-0.3855, -0.4422, 1.1399, 1.5558, 0.4781],
[ 0.1822, -0.5771, 0.2585, 0.8676, 0.2132],
[ 0.0330, 0.1084, -0.1692, -0.2771, -0.0804]])
t6 = torch.matmul(torch.transpose(t1, 0, 1), t2)
print(t6)
tensor([[ 1.7453, 0.3392],
[-1.6038, -0.2180]])
t1
tensor([[ 0.5153, -0.4414],
[-0.1939, 0.4694],
[-0.9414, 0.5997],
[-0.2057, 0.5087],
[ 0.1390, -0.1224]])
norm_t1 = torch.linalg.norm(t1, ord=2, dim=1)
print(norm_t1)
tensor([0.6785, 0.5078, 1.1162, 0.5488, 0.1853])
np.sqrt(t1[0][0]**2+t1[0][1]**2)
tensor(0.6785)
# to verify the above calculated the norm, we can do
np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(t1.numpy()), axis=1))
array([0.678, 0.508, 1.116, 0.549, 0.185], dtype=float32)
12.7. Split, stack, and concatenate tensors#
torch.manual_seed(1)
t = torch.rand(6)
print(t)
t_splits = torch.chunk(t, 3)
[item.numpy() for item in t_splits]
tensor([0.7576, 0.2793, 0.4031, 0.7347, 0.0293, 0.7999])
[array([0.758, 0.279], dtype=float32),
array([0.403, 0.735], dtype=float32),
array([0.029, 0.8 ], dtype=float32)]
torch.manual_seed(1)
t = torch.rand(5)
print(t)
t_splits = torch.split(t, split_size_or_sections=[3, 2])
[item.numpy() for item in t_splits]
tensor([0.7576, 0.2793, 0.4031, 0.7347, 0.0293])
[array([0.758, 0.279, 0.403], dtype=float32),
array([0.735, 0.029], dtype=float32)]
A = torch.ones(3)
B = torch.zeros(2)
C = torch.cat([A, B], axis=0)
print(C)
tensor([1., 1., 1., 0., 0.])
A = torch.ones(3)
B = torch.zeros(3)
S = torch.stack([A, B], axis=1)
print(S)
print(S.shape)
tensor([[1., 0.],
[1., 0.],
[1., 0.]])
torch.Size([3, 2])
12.8. Building input pipelines in PyTorch#
12.9. Creating a PyTorch DataLoader from existing tensors#
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
t = torch.arange(6, dtype=torch.float32)
print(t.shape)
data_loader = DataLoader(t)
torch.Size([6])
for item in data_loader:
print(item, item.shape)
tensor([0.]) torch.Size([1])
tensor([1.]) torch.Size([1])
tensor([2.]) torch.Size([1])
tensor([3.]) torch.Size([1])
tensor([4.]) torch.Size([1])
tensor([5.]) torch.Size([1])
data_loader = DataLoader(t, batch_size=3, drop_last=False)
for i, batch in enumerate(data_loader, 1):
print(f'batch {i}:', batch)
batch 1: tensor([0., 1., 2.])
batch 2: tensor([3., 4., 5.])
12.10. Combining two tensors into a joint dataset#
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
class JointDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
def __len__(self):
return len(self.x)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return self.x[idx], self.y[idx]
torch.manual_seed(1)
t_x = torch.rand([4, 3], dtype=torch.float32)
t_y = torch.arange(4)
#joint_dataset = JointDataset(t_x, t_y)
# Or use TensorDataset directly
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset
joint_dataset = TensorDataset(t_x, t_y)
for example in joint_dataset:
print(' x: ', example[0],
' y: ', example[1])
x: tensor([0.7576, 0.2793, 0.4031]) y: tensor(0)
x: tensor([0.7347, 0.0293, 0.7999]) y: tensor(1)
x: tensor([0.3971, 0.7544, 0.5695]) y: tensor(2)
x: tensor([0.4388, 0.6387, 0.5247]) y: tensor(3)
12.11. Shuffle, batch, and repeat#
torch.manual_seed(1)
data_loader = DataLoader(dataset=joint_dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True)
for i, batch in enumerate(data_loader, 1):
print(f'batch {i}:', 'x:', batch[0],
'\n y:', batch[1])
for epoch in range(2):
print(f'epoch {epoch+1}')
for i, batch in enumerate(data_loader, 1):
print(f'batch {i}:', 'x:', batch[0],
'\n y:', batch[1])
batch 1: x: tensor([[0.3971, 0.7544, 0.5695],
[0.7576, 0.2793, 0.4031]])
y: tensor([2, 0])
batch 2: x: tensor([[0.7347, 0.0293, 0.7999],
[0.4388, 0.6387, 0.5247]])
y: tensor([1, 3])
epoch 1
batch 1: x: tensor([[0.7576, 0.2793, 0.4031],
[0.3971, 0.7544, 0.5695]])
y: tensor([0, 2])
batch 2: x: tensor([[0.7347, 0.0293, 0.7999],
[0.4388, 0.6387, 0.5247]])
y: tensor([1, 3])
epoch 2
batch 1: x: tensor([[0.4388, 0.6387, 0.5247],
[0.3971, 0.7544, 0.5695]])
y: tensor([3, 2])
batch 2: x: tensor([[0.7576, 0.2793, 0.4031],
[0.7347, 0.0293, 0.7999]])
y: tensor([0, 1])
12.12. Creating a dataset from files on your local storage disk#
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('/content/drive')
import pathlib
imgdir_path = pathlib.Path('/content/drive/My Drive/W&M/Teaching/DATA621/cat_dog_images')
file_list = sorted([str(path) for path in imgdir_path.glob('*.jpg')])
print(file_list)
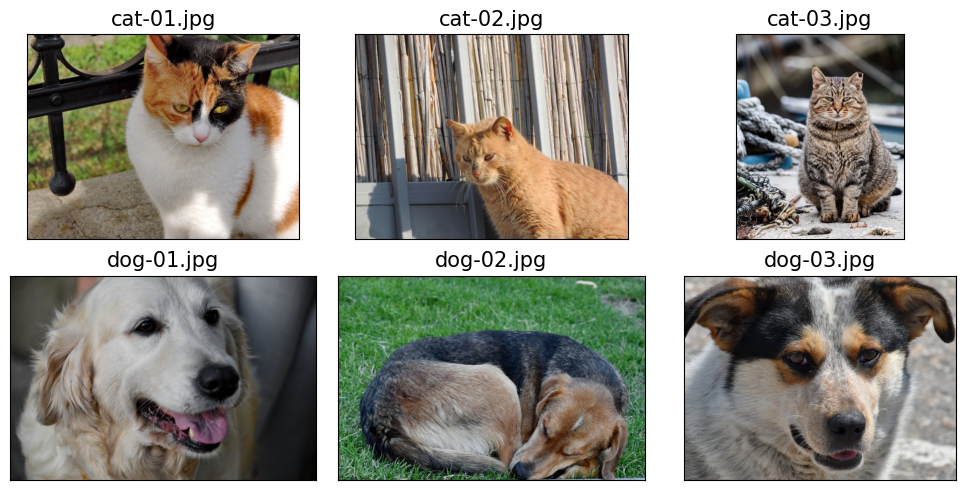
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
from PIL import Image
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
for i, file in enumerate(file_list):
img = Image.open(file)
print('Image shape: ', np.array(img).shape)
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 3, i+1)
ax.set_xticks([]); ax.set_yticks([])
ax.imshow(img)
ax.set_title(os.path.basename(file), size=15)
#plt.savefig('figures/12_03.pdf')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Image shape: (900, 1200, 3)
Image shape: (900, 1200, 3)
Image shape: (900, 742, 3)
Image shape: (800, 1200, 3)
Image shape: (800, 1200, 3)
Image shape: (900, 1200, 3)

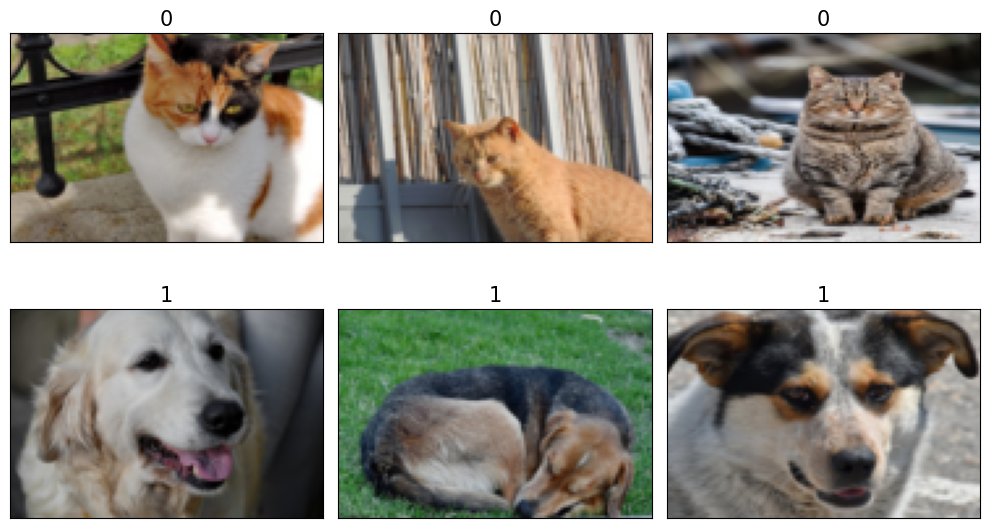
labels = [1 if 'dog' in os.path.basename(file) else 0
for file in file_list]
print(labels)
[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1]
class ImageDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, file_list, labels):
self.file_list = file_list
self.labels = labels
def __getitem__(self, index):
file = self.file_list[index]
label = self.labels[index]
return file, label
def __len__(self):
return len(self.labels)
image_dataset = ImageDataset(file_list, labels)
for file, label in image_dataset:
print(file, label)
/content/drive/My Drive/W&M/Teaching/DATA621/cat_dog_images/cat-01.jpg 0
/content/drive/My Drive/W&M/Teaching/DATA621/cat_dog_images/cat-02.jpg 0
/content/drive/My Drive/W&M/Teaching/DATA621/cat_dog_images/cat-03.jpg 0
/content/drive/My Drive/W&M/Teaching/DATA621/cat_dog_images/dog-01.jpg 1
/content/drive/My Drive/W&M/Teaching/DATA621/cat_dog_images/dog-02.jpg 1
/content/drive/My Drive/W&M/Teaching/DATA621/cat_dog_images/dog-03.jpg 1
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
class ImageDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, file_list, labels, transform=None):
self.file_list = file_list
self.labels = labels
self.transform = transform
def __getitem__(self, index):
img = Image.open(self.file_list[index])
if self.transform is not None:
img = self.transform(img)
label = self.labels[index]
print(type(img))
return img, label
def __len__(self):
return len(self.labels)
# let's resize to, e.g., 80x120
img_height, img_width = 80, 120
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Resize((img_height, img_width)),
])
image_dataset = ImageDataset(file_list, labels, transform)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
for i, example in enumerate(image_dataset):
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 3, i+1)
ax.set_xticks([]); ax.set_yticks([])
#imshow expect a numpy as argument
#The original shape (C, H, W) is transformed to (H, W, C)
# imshow expectes the channel dimension to be the last axis.
ax.imshow(example[0].numpy().transpose((1, 2,0)))
ax.set_title(f'{example[1]}', size=15)
plt.tight_layout()
#plt.savefig('figures/12_04.pdf')
plt.show()
WARNING:matplotlib.image:Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers).
<class 'torch.Tensor'>
<class 'torch.Tensor'>
<class 'torch.Tensor'>
<class 'torch.Tensor'>
<class 'torch.Tensor'>
<class 'torch.Tensor'>