Reference:
Sebastian Raschka, Yuxi Hayden Liu, and Vahid Mirjalili. Machine Learning with PyTorch and Scikit-Learn: Develop machine learning and deep learning models with Python. Packt Publishing Ltd, 2022.
6. Adaline (Adaptive Linear Neuron)#
from IPython.display import Image
from IPython.display import display
display(Image(url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cfteach/NNDL_DATA621/webpage-src/DATA621/DATA621/images/adaline_flowchart.png", width=700))

import numpy as np
class Adaline:
"""Perceptron classifier.
Parameters
------------
eta : float
Learning rate (between 0.0 and 1.0)
n_iter : int
Passes over the training dataset.
random_state : int
Random number generator seed for random weight
initialization.
Attributes
-----------
w_ : 1d-array
Weights after fitting.
b_ : Scalar
Bias unit after fitting.
losses_ : list
Mean squared error loss values at each epoch
"""
def __init__(self, eta=0.01, n_iter=50, random_state=1):
self.eta = eta
self.n_iter = n_iter
self.random_state = random_state
def fit(self, X, y):
"""Fit training data.
Parameters
----------
X : {array-like}, shape = [n_examples, n_features]
Training vectors, where n_examples is the number of examples and
n_features is the number of features.
y : array-like, shape = [n_examples]
Target values.
Returns
-------
self : object
"""
rgen = np.random.RandomState(self.random_state)
self.w_ = rgen.normal(loc=0.0, scale=0.01, size=X.shape[1])
self.b_ = np.float_(0.)
self.losses_ = []
for i in range(self.n_iter):
net_input = self.net_input(X)
output = self.activation(net_input)
errors = (y-output)
# the following is vectorized
self.w_ += self.eta * 2.0 * X.T.dot(errors) / X.shape[0] #[n_features,n_examples]*[n_examples] = [n_features]
self.b_ += self.eta * 2.0 * errors.mean()
loss = (errors**2).mean()
self.losses_.append(loss)
return self
def net_input(self, X):
"""Calculate net input"""
return np.dot(X, self.w_) + self.b_
def activation(self, X):
"""Compute linear activation"""
return X
def predict(self, X):
"""Return class label after unit step"""
return np.where(self.activation(self.net_input(X)) >= 0.5, 1, 0)
6.1. Using the Iris data#
import os
import pandas as pd
try:
s = 'https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/iris/iris.data'
print('From URL:', s)
df = pd.read_csv(s,
header=None,
encoding='utf-8')
except HTTPError:
s = 'iris.data'
print('From local Iris path:', s)
df = pd.read_csv(s,
header=None,
encoding='utf-8')
df.tail()
From URL: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/iris/iris.data
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145 | 6.7 | 3.0 | 5.2 | 2.3 | Iris-virginica |
| 146 | 6.3 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 1.9 | Iris-virginica |
| 147 | 6.5 | 3.0 | 5.2 | 2.0 | Iris-virginica |
| 148 | 6.2 | 3.4 | 5.4 | 2.3 | Iris-virginica |
| 149 | 5.9 | 3.0 | 5.1 | 1.8 | Iris-virginica |
6.2. Plotting the Iris data#
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# select setosa and versicolor
#y = df.iloc[0:100, 4].values
y = df.iloc[:, 4].values
X = df.iloc[:, [0, 2]].values # extract sepal length and petal length
# Map y values to 0, 1, or -1
y_mapped = np.select(
[y == 'Iris-setosa', y == 'Iris-versicolor'], # Conditions
[0, 1], # Values to assign if the condition is True
default=-1 # Value to assign if none of the conditions are True
)
mask = (y_mapped == 0) | (y_mapped == 1) # Mask for selecting only 0 and 1 in y_mapped
X_filtered = X[mask]
y_filtered = y_mapped[mask]
# Filter the first 50 occurrences of category 0
mask_0 = (y_filtered == 0)
X_0 = X_filtered[mask_0][:50]
# Filter the first 50 occurrences of category 1
mask_1 = (y_filtered == 1)
X_1 = X_filtered[mask_1][:50]
print(np.shape(X_0))
print(np.shape(X_1))
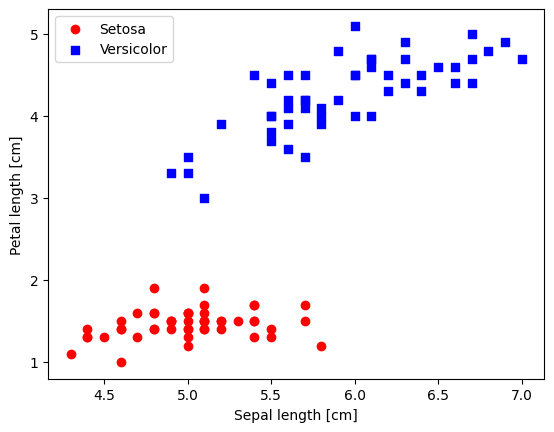
# plot data
plt.scatter(X_0[:, 0], X_0[:, 1],
color='red', marker='o', label='Setosa')
plt.scatter(X_1[:, 0], X_1[:, 1],
color='blue', marker='s', label='Versicolor')
plt.xlabel('Sepal length [cm]')
plt.ylabel('Petal length [cm]')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
(50, 2)
(50, 2)
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7fe443663100>
6.3. Training the Adaline model#
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(10, 4))
ada1 = Adaline(n_iter=15, eta=0.1).fit(X_filtered, y_filtered)
ax[0].plot(range(1, len(ada1.losses_) + 1), np.log10(ada1.losses_), marker='o')
ax[0].set_xlabel('Epochs')
ax[0].set_ylabel('log(Mean squared error)')
ax[0].set_title('Adaline - Learning rate 0.1')
ada2 = Adaline(n_iter=15, eta=0.0001).fit(X_filtered, y_filtered)
ax[1].plot(range(1, len(ada2.losses_) + 1), ada2.losses_, marker='o')
ax[1].set_xlabel('Epochs')
ax[1].set_ylabel('Mean squared error')
ax[1].set_title('Adaline - Learning rate 0.0001')
plt.show()
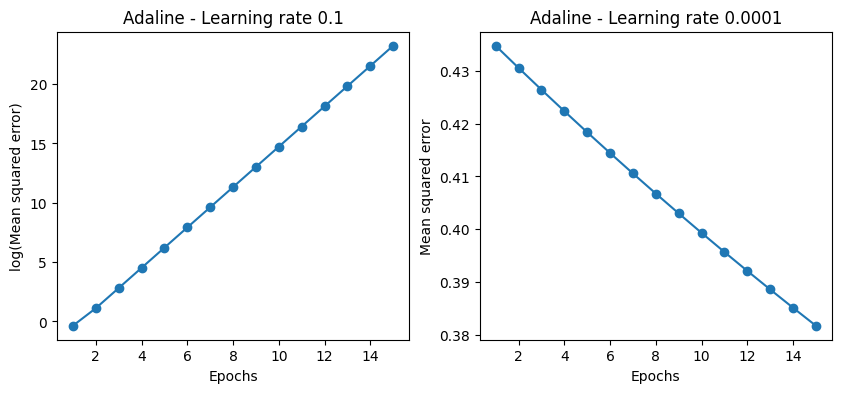
Plot on the left shows that the learning rate is too high, the one on the right that the learning rate is too low.
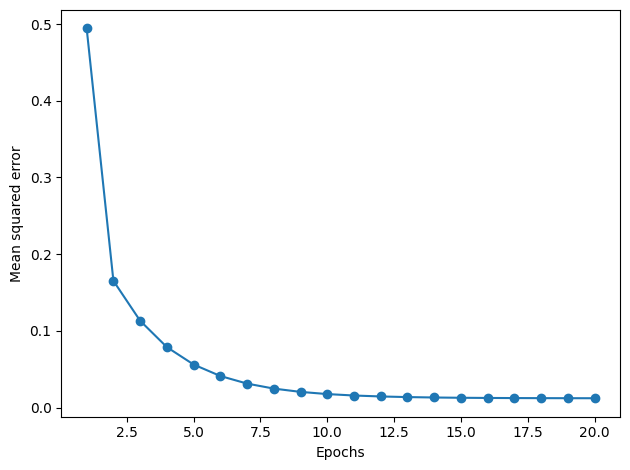
6.4. Standardize Data#
This can be very helpful: gradient descent is one of many algorithms that benefit from feature scaling.
X_std = np.copy(X_filtered)
X_std[:,0] = (X_filtered[:,0]-X_filtered[:,0].mean())/X_filtered[:,0].std()
X_std[:,1] = (X_filtered[:,1]-X_filtered[:,1].mean())/X_filtered[:,1].std()
ada_gd = Adaline(n_iter=20, eta=0.5).fit(X_std, y_filtered)
plt.plot(range(1, len(ada_gd.losses_) + 1), ada_gd.losses_, marker='o')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Mean squared error')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
6.5. Plotting decision regions#
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
def plot_decision_regions(X, y, classifier, resolution=0.02):
# setup marker generator and color map
markers = ('o', 's', '^', 'v', '<')
colors = ('red', 'blue', 'lightgreen', 'gray', 'cyan')
cmap = ListedColormap(colors[:len(np.unique(y))])
# plot the decision surface
x1_min, x1_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
x2_min, x2_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx1, xx2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x1_min, x1_max, resolution),
np.arange(x2_min, x2_max, resolution))
lab = classifier.predict(np.array([xx1.ravel(), xx2.ravel()]).T)
lab = lab.reshape(xx1.shape)
plt.contourf(xx1, xx2, lab, alpha=0.3, cmap=cmap)
plt.xlim(xx1.min(), xx1.max())
plt.ylim(xx2.min(), xx2.max())
# plot class examples
for idx, cl in enumerate(np.unique(y)):
plt.scatter(x=X[y == cl, 0],
y=X[y == cl, 1],
alpha=0.8,
c=colors[idx],
marker=markers[idx],
label=f'Class {cl}',
edgecolor='black')
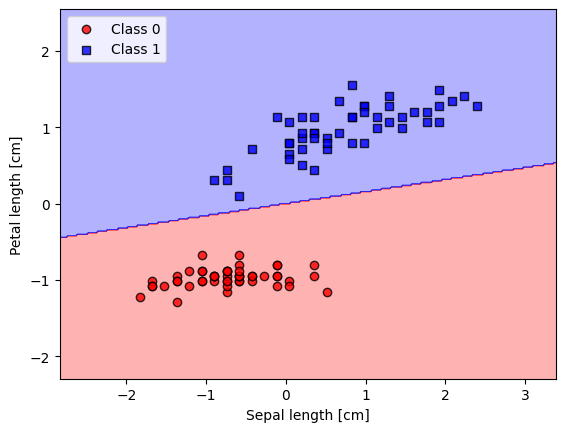
plot_decision_regions(X_std, y_filtered, classifier=ada_gd)
plt.xlabel('Sepal length [cm]')
plt.ylabel('Petal length [cm]')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show()
6.6. Accuracy#
y_pred = ada_gd.predict(X_std)
accuracy = np.sum(y_pred == y_filtered) / len(y_filtered)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy * 100:.2f}%")
Accuracy: 100.00%